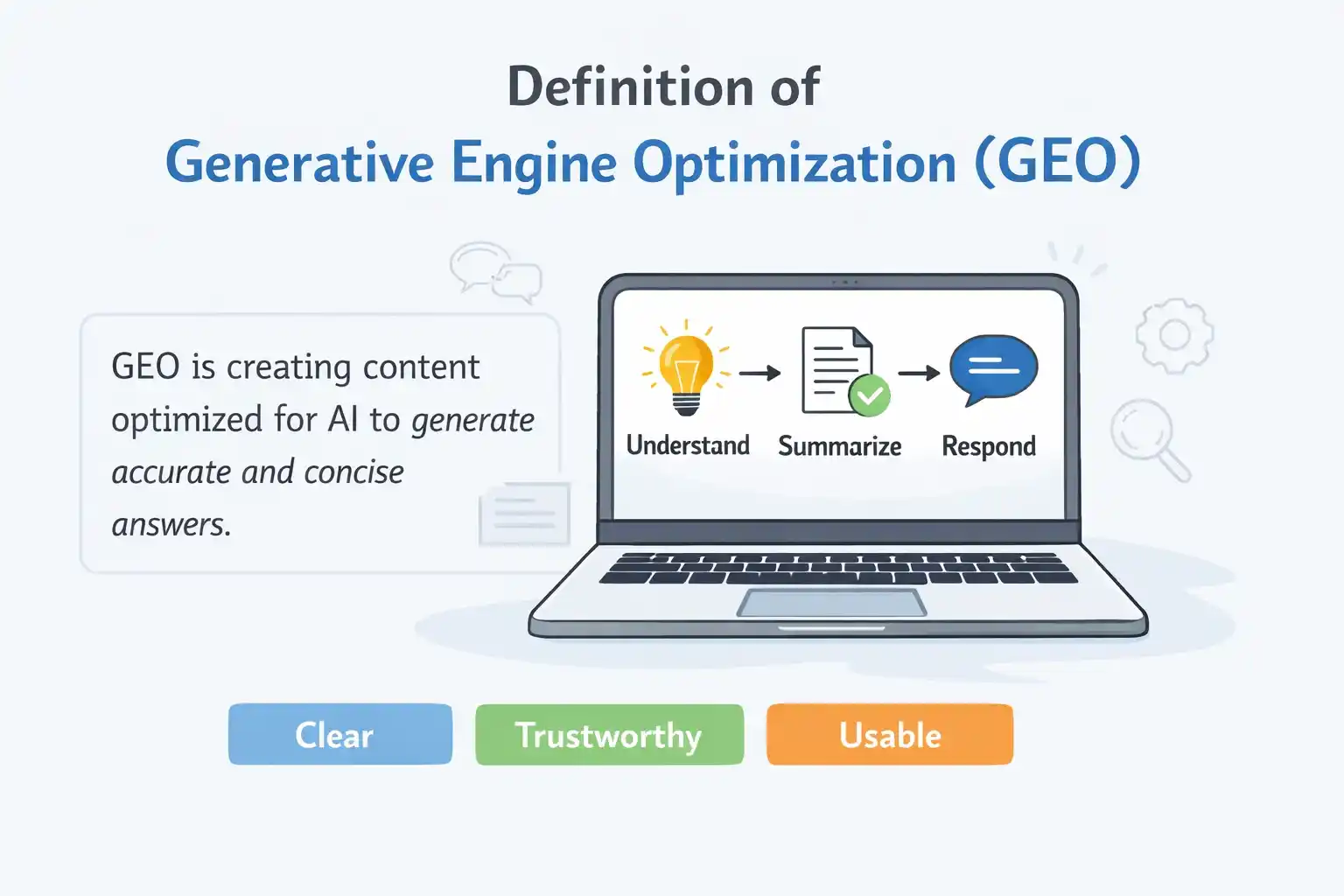
What Is The Definition of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, is the process of preparing content in a way that allows AI-driven systems to select and present it as part of their responses. The focus is not just on search engine rankings, but on making content understandable and dependable for AI-generated answers. Its purpose is to support the delivery of trustworthy information through AI search experiences.
Negative Effects of GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) OR Disadvantages of GEO

- Reduced Website Traffic
- Loss of Content Ownership
- Over-Simplified Content
- Ranking and Visibility Uncertainty
- Weak Focus on Real User Intent
- Summary
Reduced Website Traffic
AI tools often give complete answers directly, so users don’t visit websites. This decreases organic traffic, clicks, and potential leads.
Loss of Content Ownership
AI-generated summaries may use your content without clear credit, reducing brand visibility and authority.
Over-Simplified Content
GEO pushes content to be brief and generic, which lowers depth, originality, and strong keyword coverage needed for SEO.
Ranking and Visibility Uncertainty
AI citations change frequently and are hard to track, making performance less predictable than traditional SEO rankings.
Weak Focus on Real User Intent
Content written mainly for AI systems considered can ignore real user needs, harming long-term SEO performance.
Summary: GEO offers AI exposure, but relying on it too much can negatively impact traffic, authority, and sustainable SEO growth.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) vs. Hand-Written Content: Keyword Differences
1. Keyword Searching
GEO:
Keywords are generated from prompts, AI models, and predictive patterns. They are based on how AI systems understand questions, context, and entities rather than how real users type queries.Hand-Written Content:
Keywords come from manual research, real user searches, client queries, and practical experience. Writers choose terms that people naturally use on Google or other search engines.
2. Search Intent Understanding
GEO:
Focuses on inferred intent. Keywords are structured to help AI engines summarize, recommend, or cite content in generated answers.Hand-Written Content:
Targets clear human intent such as informational, transactional, or navigational searches. Keywords reflect what users actually want to read, buy, or learn.
3. Keyword Structure"Manual or auto"
GEO:
Mostly long, conversational, and question-based phrases. Keywords are optimized for natural language processing and AI comprehension.Hand-Written Content:
Uses a balanced mix of short-tail, mid-tail, and long-tail keywords. Structure is simple, readable, and aligned with traditional SEO practices.
4. Semantic Depth vs. Narrative Context
GEO:
Relies heavily on semantic relationships and entity linking. Keywords are placed to help AI understand topic depth rather than keyword frequency.Hand-Written Content:
Uses contextual keywords naturally within paragraphs, headings, and examples. Semantics are built through storytelling, explanations, and real scenarios.
5. Keyword Flexibility"AI or Deep Search"
GEO:
Keywords are flexible and adaptive. AI-driven content can change phrasing quickly based on new prompts or updated models.Hand-Written Content:
Keywords are more stable. Writers refine and update them based on performance data, trends, and reader feedback over time.
6. Trust & Authenticity Signals
GEO:
Keywords aim to appear relevant to AI systems, but may lack lived experience or originality if not guided carefully.Hand-Written Content:
Keywords are supported by personal insight, expertise, and unique opinions, which increases trust, credibility, and long-term value.
7. Optimization Goal
GEO:
The main goal is visibility inside AI-generated answers, summaries, and recommendation engines.Hand-Written Content:
The goal is ranking on search engines, engaging readers, and converting traffic into leads, sales, or loyal audiences.
8. Risk & Sustainability
GEO:
Over-optimized or synthetic keywords may become less effective as AI models evolve or filtering improves.Hand-Written Content:
Human-researched keywords remain sustainable because they are rooted in real user behavior and genuine content needs.
Leave a Reply